Trigonometric identities

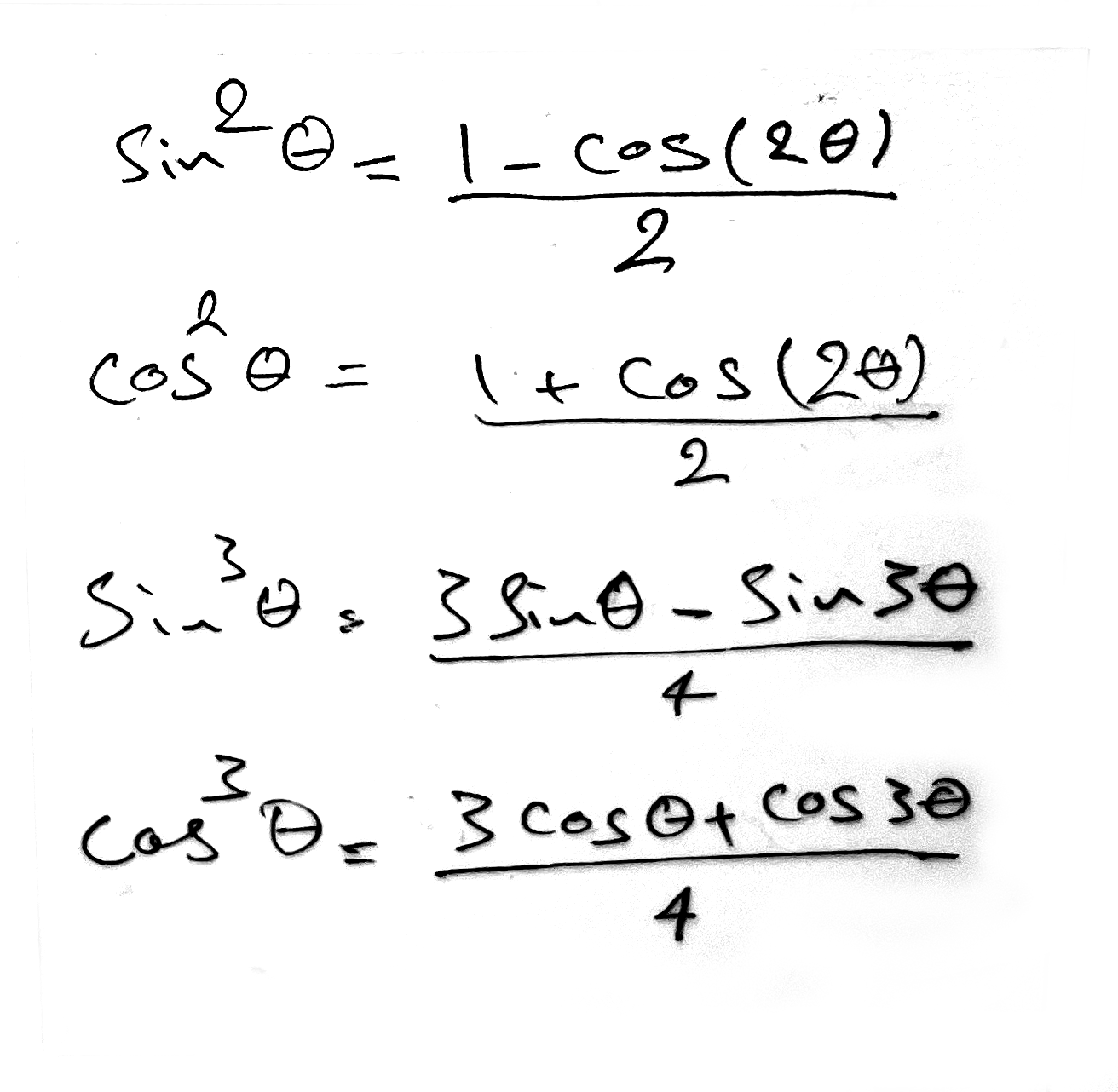

Fundamental Identities
Pythagorean Identities
- sin²θ + cos²θ = 1
- tan²θ + 1 = sec²θ
- 1 + cot²θ = csc²θ
Reciprocal Identities
- sin θ = 1/csc θ
- cos θ = 1/sec θ
- tan θ = 1/cot θ
- csc θ = 1/sin θ
- sec θ = 1/cos θ
- cot θ = 1/tan θ
Quotient Identities
- tan θ = sin θ/cos θ
- cot θ = cos θ/sin θ
Compound Angle Formulas
Sum and Difference Formulas
- sin(α ± β) = sin α cos β ± cos α sin β
- cos(α ± β) = cos α cos β ∓ sin α sin β
- tan(α ± β) = (tan α ± tan β)/(1 ∓ tan α tan β)
Double Angle Formulas
- sin(2θ) = 2sin θ cos θ
- cos(2θ) = cos²θ - sin²θ = 2cos²θ - 1 = 1 - 2sin²θ
- tan(2θ) = 2tan θ/(1 - tan²θ)
Triple Angle Formulas
- sin(3θ) = 3sin θ - 4sin³θ
- cos(3θ) = 4cos³θ - 3cos θ
Half Angle Formulas
- sin(θ/2) = ±√[(1 - cos θ)/2] (sign depends on quadrant)
- cos(θ/2) = ±√[(1 + cos θ)/2] (sign depends on quadrant)
- tan(θ/2) = (1 - cos θ)/sin θ = sin θ/(1 + cos θ)
Product to Sum Formulas
- sin α sin β = (1/2)[cos(α - β) - cos(α + β)]
- cos α cos β = (1/2)[cos(α - β) + cos(α + β)]
- sin α cos β = (1/2)[sin(α + β) + sin(α - β)]
Sum to Product Formulas
- sin α + sin β = 2sin((α + β)/2)cos((α - β)/2)
- sin α - sin β = 2cos((α + β)/2)sin((α - β)/2)
- cos α + cos β = 2cos((α + β)/2)cos((α - β)/2)
- cos α - cos β = -2sin((α + β)/2)sin((α - β)/2)
Power Reduction Formulas
- sin²θ = (1 - cos(2θ))/2
- cos²θ = (1 + cos(2θ))/2
- sin³θ = (3sin θ - sin(3θ))/4
- cos³θ = (3cos θ + cos(3θ))/4
Application Strategies
For Proving Identities
- Start with the more complex side
- Use fundamental identities to simplify
- Transform to look like the other side
- Avoid working with both sides simultaneously
For Solving Trigonometric Equations
- Express everything in terms of a single function (e.g., all in sin θ)
- Apply algebraic methods (factoring, completing square, etc.)
- Find all solutions within the principal interval
- Extend to full domain if needed
Example: Showing 4sin²x cos²x = (1-cos(4x))/2
- Use sin(2x) = 2sin x cos x
- 4sin²x cos²x = (2sin x cos x)²
- = sin²(2x)
- Apply sin²θ = (1 - cos(2θ))/2
- = (1 - cos(4x))/2
Example: Solving sin x cos x + 1 = 0
- Use sin(2x) = 2sin x cos x
- sin(2x)/2 + 1 = 0
- sin(2x) = -2
-
Since sin θ ≤ 1, this has no solution
See: