Trigonometric functions


 ![[Screenshot 2025-02-20 at 15.39.20.png]
![[Screenshot 2025-02-20 at 15.39.20.png]
Core Functions and Their Properties
Basic Definitions
- Sine (sin): In a right triangle, sin(θ) = opposite/hypotenuse
- Cosine (cos): In a right triangle, cos(θ) = adjacent/hypotenuse
- Tangent (tan): In a right triangle, tan(θ) = opposite/adjacent = sin(θ)/cos(θ)
- Cotangent (cot): cot(θ) = 1/tan(θ) = cos(θ)/sin(θ)
- Secant (sec): sec(θ) = 1/cos(θ)
- Cosecant (csc): csc(θ) = 1/sin(θ)
Domains and Ranges
- sin(x): Domain: ℝ, Range: [-1, 1]
- cos(x): Domain: ℝ, Range: [-1, 1]
-
tan(x): Domain: {x ∈ ℝ x ≠ π/2 + nπ}, Range: ℝ -
cot(x): Domain: {x ∈ ℝ x ≠ nπ}, Range: ℝ -
sec(x): Domain: {x ∈ ℝ x ≠ π/2 + nπ}, Range: (-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞) -
csc(x): Domain: {x ∈ ℝ x ≠ nπ}, Range: (-∞, -1] ∪ [1, ∞)
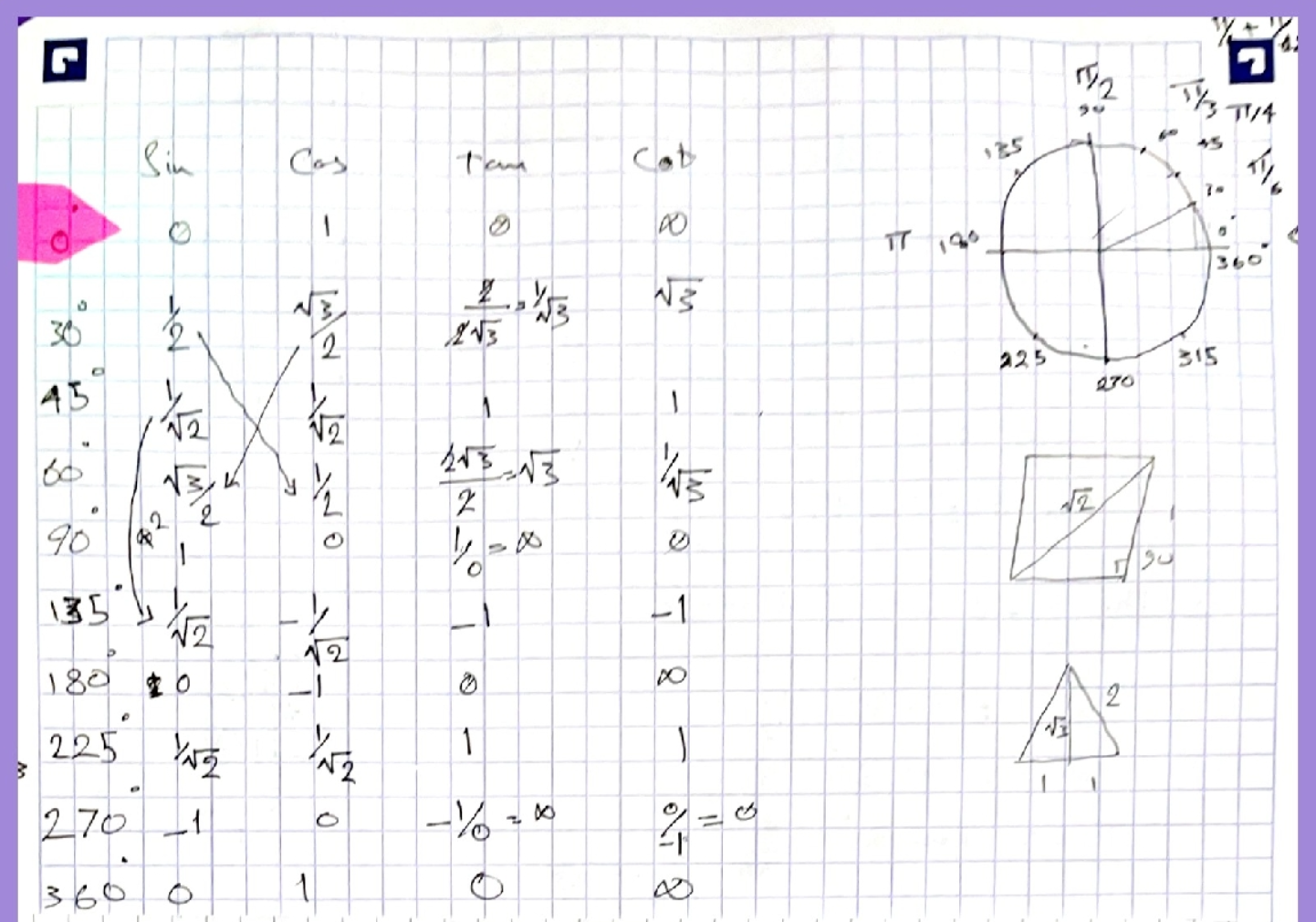
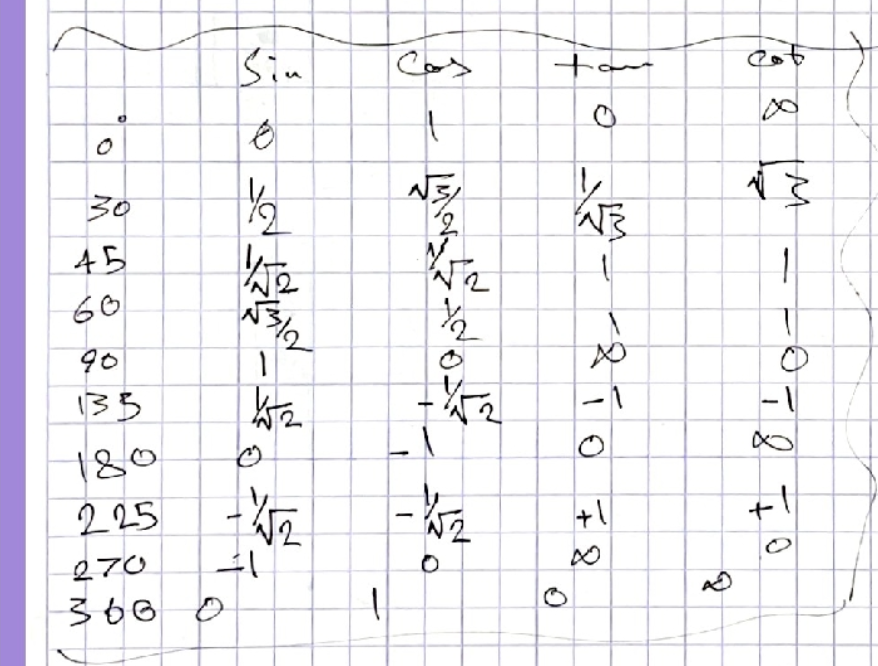
Key Function Values
| Angle (θ) | sin(θ) | cos(θ) | tan(θ) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| π/6 (30°) | 1/2 | √3/2 | 1/√3 |
| π/4 (45°) | 1/√2 | 1/√2 | 1 |
| π/3 (60°) | √3/2 | 1/2 | √3 |
| π/2 (90°) | 1 | 0 | undef. |
| π (180°) | 0 | -1 | 0 |
| 3π/2 (270°) | -1 | 0 | undef. |
| 2π (360°) | 0 | 1 | 0 |
Periodicity
- sin(x + 2π) = sin(x)
- cos(x + 2π) = cos(x)
- tan(x + π) = tan(x)
- cot(x + π) = cot(x)
- sec(x + 2π) = sec(x)
- csc(x + 2π) = csc(x)
Trigonometric Function Properties
Evenness and Oddness
- sin(-x) = -sin(x) (odd function)
- cos(-x) = cos(x) (even function)
- tan(-x) = -tan(x) (odd function)
- cot(-x) = -cot(x) (odd function)
- sec(-x) = sec(x) (even function)
- csc(-x) = -csc(x) (odd function)
Derivatives
- d/dx[sin(x)] = cos(x)
- d/dx[cos(x)] = -sin(x)
- d/dx[tan(x)] = sec²(x)
- d/dx[cot(x)] = -csc²(x)
- d/dx[sec(x)] = sec(x)tan(x)
- d/dx[csc(x)] = -csc(x)cot(x)
Integrals
- ∫sin(x)dx = -cos(x) + C
- ∫cos(x)dx = sin(x) + C
-
∫tan(x)dx = -ln cos(x) + C -
∫cot(x)dx = ln sin(x) + C -
∫sec(x)dx = ln sec(x) + tan(x) + C -
∫csc(x)dx = ln csc(x) - cot(x) + C
Solving Trigonometric Inequalities
Basic Approach
- Isolate the trigonometric expression
- Find critical points by solving the corresponding equation
- Test intervals between critical points
- Express the solution in terms of the appropriate interval
Examples for Solving Inequalities like 2sin²x > 1
For 2sin²x > 1:
- Divide both sides by 2: sin²x > 1/2
-
Take square root: sin x > 1/√2 - Solve: sin x > 1/√2 or sin x < -1/√2
- Find all solutions in [0, 2π]:
- sin x > 1/√2 gives x ∈ (π/4, 3π/4)
- sin x < -1/√2 gives x ∈ (5π/4, 7π/4)
- Extend to all reals: x ∈ (π/4 + 2nπ, 3π/4 + 2nπ) ∪ (5π/4 + 2nπ, 7π/4 + 2nπ), where n ∈ ℤ
For 4sin x cos x + 1 < 0
- Use identity: sin(2x) = 2sin x cos x
- Rewrite: 2sin(2x) + 1 < 0
- Solve: sin(2x) < -1/2
- Find solutions in [0, 4π]:
- 2x ∈ (7π/6 + 2nπ, 11π/6 + 2nπ), where n ∈ ℤ
- x ∈ (7π/12 + nπ, 11π/12 + nπ), where n ∈ ℤ
Special Triangle Relationships
30-60-90 Triangle
- If the shortest leg length is a:
- The hypotenuse is 2a
- The longer leg is a√3
45-45-90 Triangle
- If the leg length is a:
- The hypotenuse is a√2
- Both legs are equal (a)
See
- Trigonometric Identities
- Trigonometric Equations
- Trigonometric Inequalities
- 30-60-90 Triangle
- 45-45-90 Triangle
- Derivatives - For derivatives of trigonometric functions
- Integration Techniques - For integration of trigonometric functions
Exercises
- Solve trigonometric inequalities like $2\sin^2 x > 1$, $\cos^2 x \leq 1$, $4\sin x \cos x + 1 < 0$.